| Type |
Definition |
Construction |
Operation Principle |
Components |
Applications |
| Lead-Acid Batteries |
Rechargeable battery with lead plates and sulfuric acid. |
Consists of lead plates and sulfuric acid in a plastic case. |
Energy stored via chemical reaction, available on demand. |
Lead, lead dioxide, sulfuric acid. |
Used in automotive, UPS, and solar applications. |
| Type |
Definition |
Construction |
Operation Principle |
Components |
Applications |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries |
Rechargeable batteries where lithium ions move between electrodes during discharge and charge. |
Cathode (lithium metal oxide), anode (carbon), electrolyte, separator. |
Lithium ions move through an organic solvent electrolyte between cathode and anode. |
Lithium metal oxides, carbon/graphite, organic solvent. |
Portable electronics, electric vehicles, renewable energy storage. |
| Nickel-Cadmium Batteries |
Rechargeable batteries using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium. |
Nickel and cadmium electrodes in an alkaline electrolyte. |
Oxidation-reduction reactions between cadmium and nickel compounds. |
Nickel oxide hydroxide, cadmium, alkaline electrolyte. |
Power tools, photography equipment, emergency lighting. |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries |
Similar to nickel-cadmium but with a hydrogen-absorbing alloy replacing cadmium. |
Metal hydride negative electrode, nickel hydroxide positive electrode. |
Hydrogen ions move between electrodes, facilitating charge and discharge. |
Nickel hydroxide, metal hydride alloy, alkaline electrolyte. |
Hybrid vehicles, high-drain electronics, digital cameras. |
| Alkaline Batteries |
Primary batteries dependent on the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide. |
Zinc powder anode, manganese dioxide cathode, alkaline electrolyte. |
Electrochemical reaction of zinc with manganese dioxide produces energy. |
Zinc, manganese dioxide, alkaline potassium hydroxide. |
Remote controls, flashlights, toys, and portable electronics. |
| Image |
Description |

|
This image illustrates the basic knowledge and classification of lead-acid batteries.
|
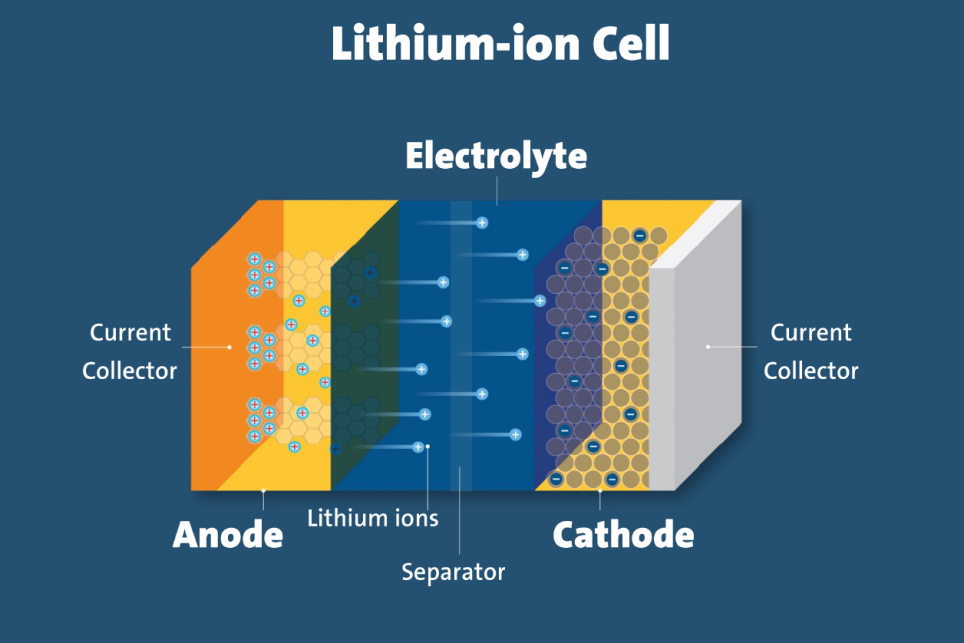
|
This image shows the structure of a lithium-ion cell, highlighting its components.
|

|
This image provides a composition breakdown of a nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery.
|

|
This image details the principle structure and material composition of a nickel-cadmium battery.
|
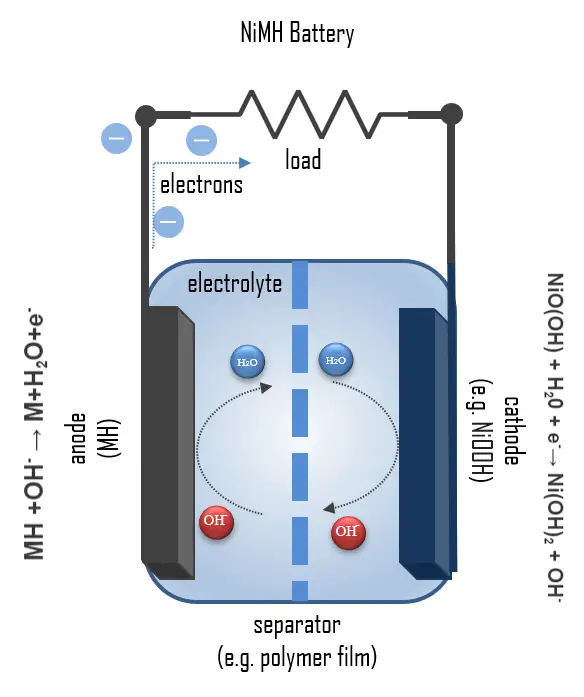
|
This image explains the principle of operation for a nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) battery.
|

|
This image highlights the design and structure of alkaline batteries.
|
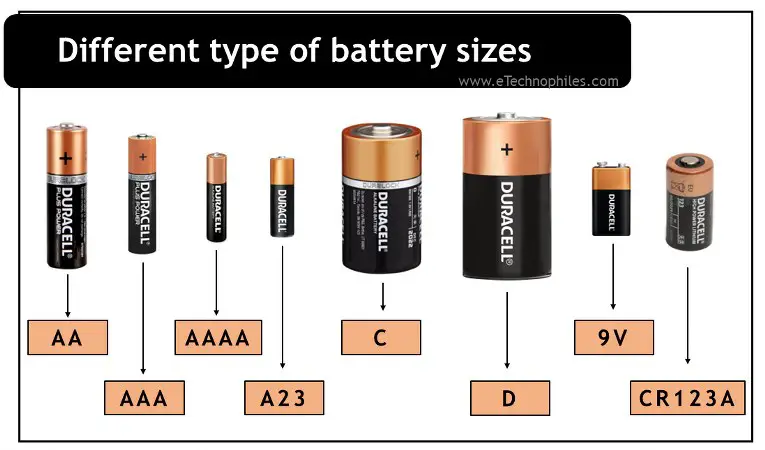
|
This image compares various battery sizes and their typical applications.
|







